India Supreme Court says it may strike down law banning gay sex
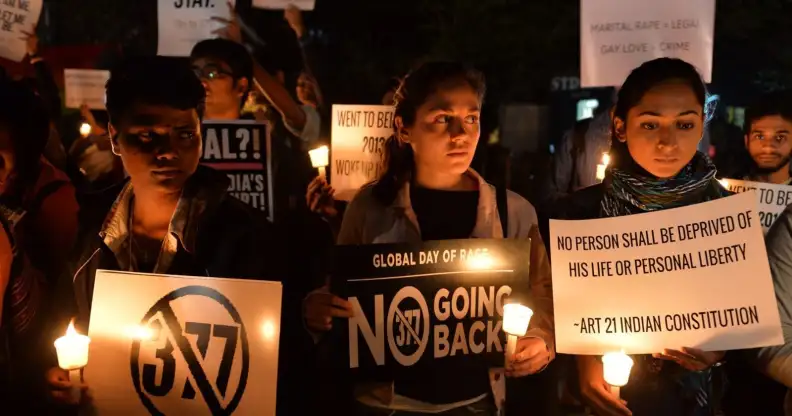
Indian activists demonstrate against the Supreme Court’s reinstatement of Section 377 in 2014 (Manjunath Kiran/AFP/Getty)
India’s Supreme Court has signalled that it could strike down the country’s sodomy law.
Colonial-era penal code Section 377, which criminalises sex “against the order of nature,” has been widely used to clamp down on the LGBT community in India, which is home to 1.3 billion people.
LGBT campaigners have been calling for the repeal of the law since it was brought back into effect by a court ruling in 2013.
The country’s Supreme Court is currently hearing a case relating to the law, and there have been a number of positive signs indicating that justices could strike down the anti-gay law.
Today the five-judge bench headed by Chief Justice Dipak Misra reserved their judgment on the issue, delaying a conclusion of the case until after further arguments are heard on Friday.
However the justices signalled that if Section 377 is found to violate human rights, they will not hesitate to directly strike the law down – rather than wait for the country’s Parliament to act to comply with the ruling.
According to DNA India they warned: “We would not wait for the government to repeal, amend or not to enact any law to deal with violations of fundamental rights.
“The moment we are convinced about violation of the fundamental right, the object of these fundamental rights give power to the court to strike down the law.”

A protest against Section 377 of Indian Penal Code (ARUN SANKAR/AFP/Getty)
The court last year appeared to affirm that LGBT people deserve a basic right to a private life in a separate, limited ruling – raising campaigners’ hopes.
The Indian government recently said it would leave it up to the courts to decide whether gay sex should remain criminalised.
Appearing in court last week, representatives for the Indian government declined to pick a side on the issue.
Additional Solicitor General of India Tushar Mehta said: “So far as the constitutional validity [of] Section 377 to the extent it applies to ‘consensual acts of adults in private’ is concerned, the Union of India would leave the said question to the wisdom of this Court.”
However, he pressed the court to stay confined to the issue and not rule on further rights, such as recognition for same-sex relationships.
Mehta said: ”If this Court is pleased to decide to examine any other question other than the constitutional validity of Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code, or to construe any other right in favour of or in respect of LGBTQ, the Union of India would like to file its detailed affidavit in reply as consideration of other issues would have far reaching and wide ramifications.”
The decision to sit out the battle suggests the government will not resist if the court strikes down the law.
Prime Minister Modi’s nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party MPs had resisted bids to repeal the law through Parliament, and in 2016 a private members’ bill on the issue was voted down.
Modi’s Home Secretary Rajnath Singh insisted previously: “We support Section 377 because we believe that homosexuality is [an] unnatural act that cannot be supported.”

Protesters against Section 377 (PRAKASH SINGH/AFP/Getty Images)
Shocking statistics previously showed that hundreds of men were being arrested under the reinstated anti-gay law, raising fears of a homophobic purge.
Anjali Gopalan, founder of the Naz Foundation, an NGO working to prevent HIV/AIDS in New Delhi NGO, which lodged the first petition against the 1861 law in 2001, told the Guardian that the moment “feels right” to overturn the ban on gay sex.
“The momentum has built up for this moment. We have a clutch of petitions from people from all walks of life. We have celebrities giving their personal testimony,” Gopalan said.
“Then we have had an important ruling recently by the courts upholding privacy. And we have seen a shift in recent years, more people coming out to take a stand. The gates have opened, as it were, and you can’t close them now.”

Protesters against Section 377 (SAJJAD HUSSAIN/AFP/Getty Images)
Another LGBT+ rights campaigner, Row Kavi, told the Guardian that the momentum for change was “unstoppable.”
He explained the impact of the supreme court overturning the 2009 ruling, saying: “We got calls from parents, concerned about what would happen to their children. We got calls from HR managers in companies asking if the police might come and arrest employees who had come out.”
The campaign for decriminalising gay sex also been bolstered by a supreme court ruling in August last year, which ruled that privacy, including a person’s sexuality, was a fundamental right.
Speaking to the Guardian,Suraj Sanap, the supreme court lawyer for this ruling, said: “The supreme court’s ruling on privacy last year was critical. It was a de facto overturning of its own earlier 2013 ruling against gay sex.
“That means there is really no leeway for the judges to argue otherwise than for gay sex to be legalised.”

